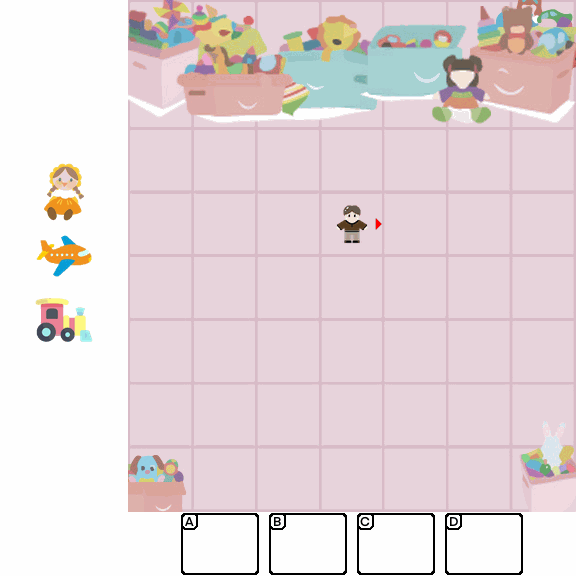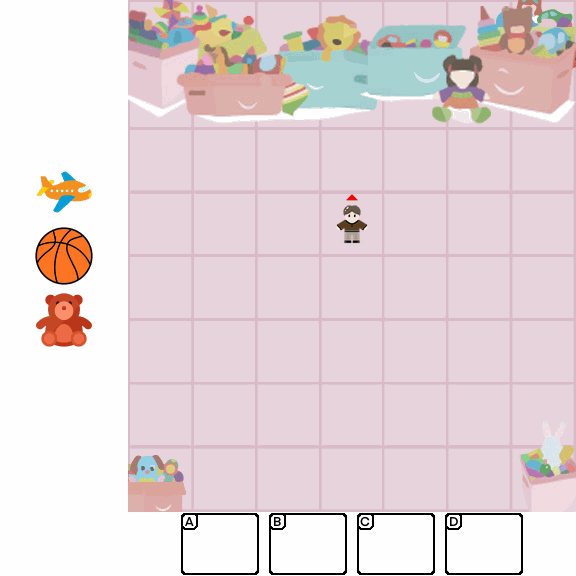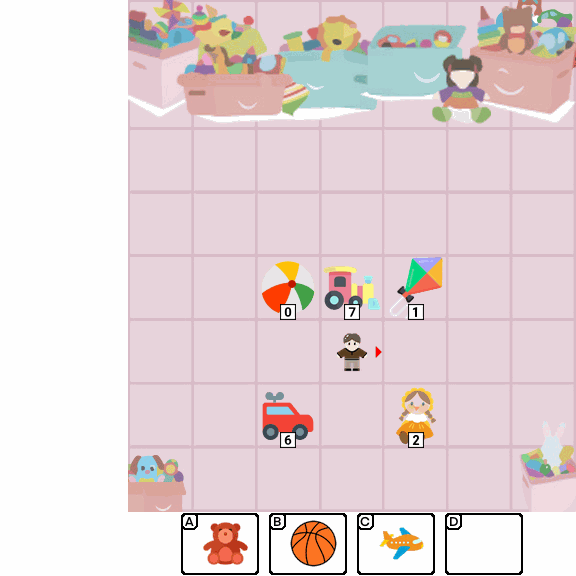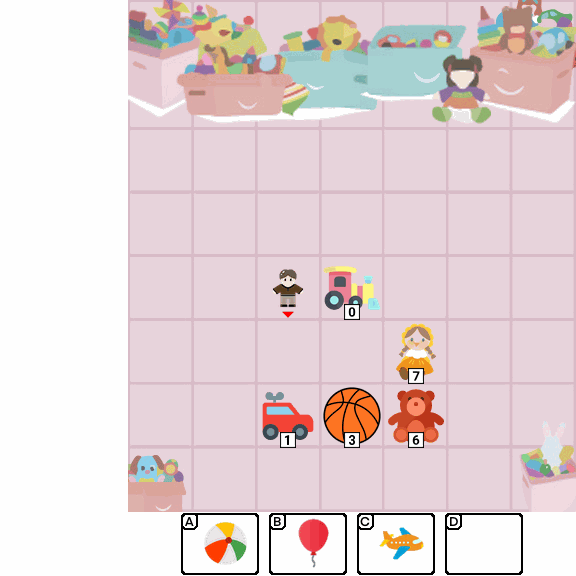
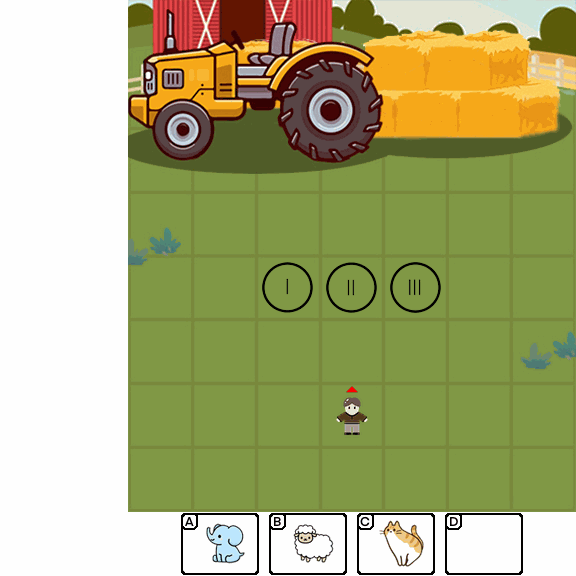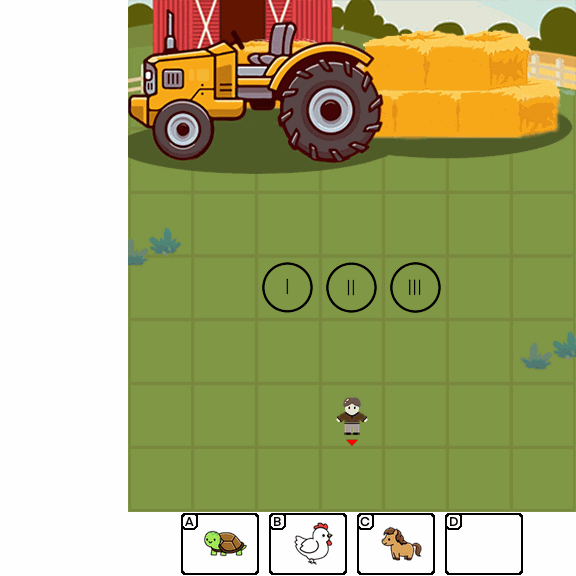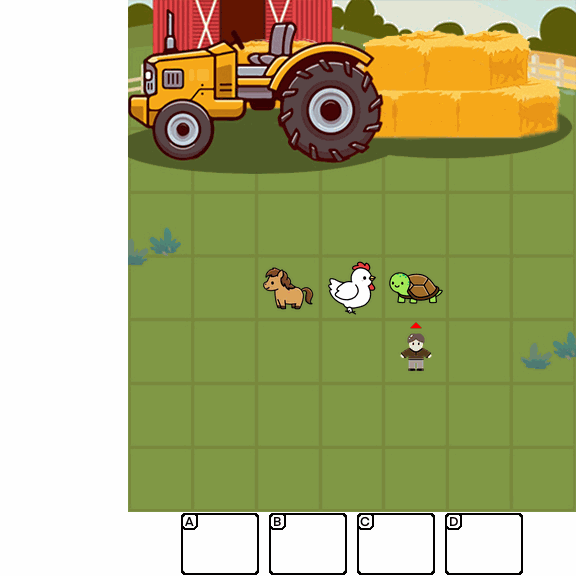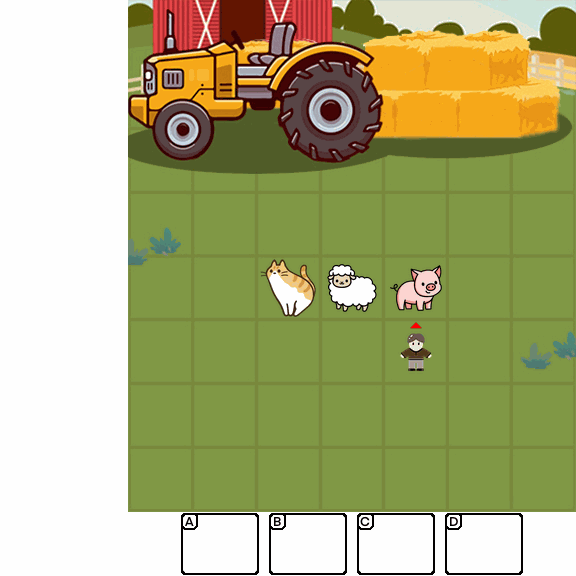
Abstract
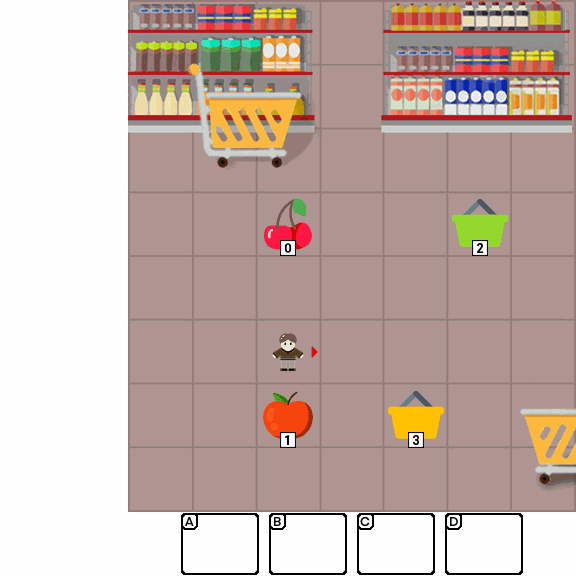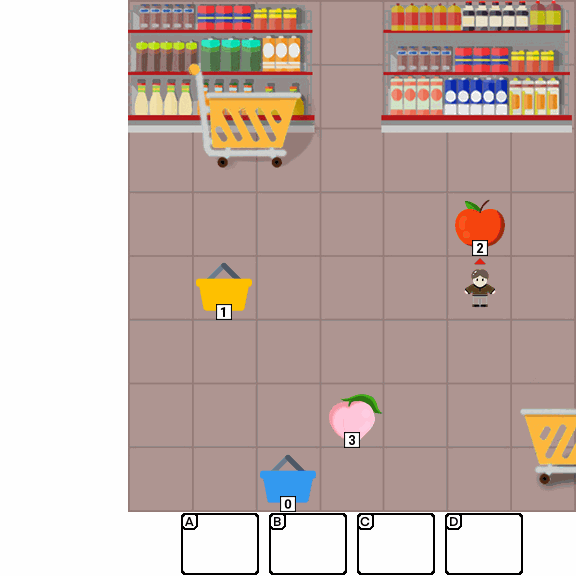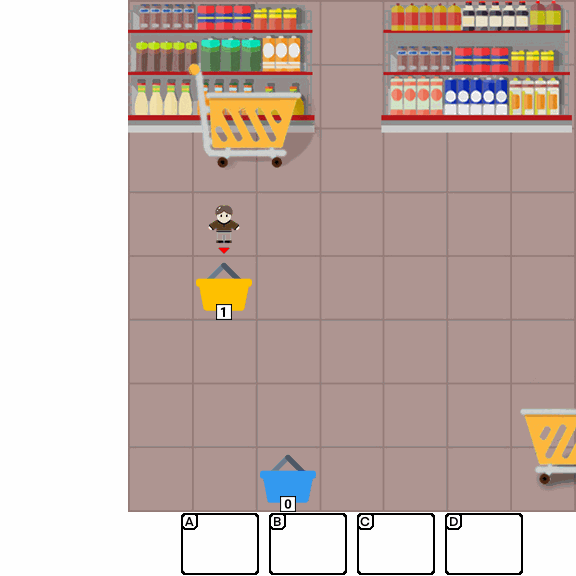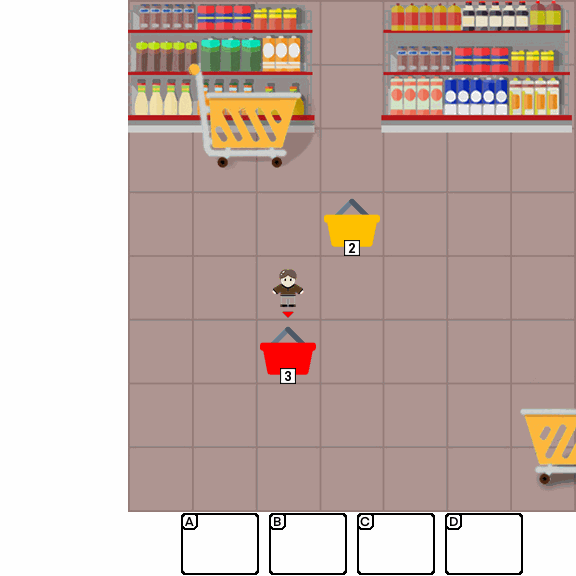
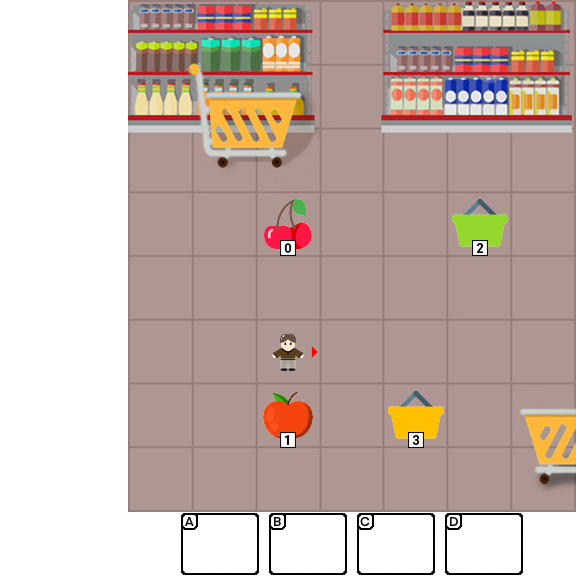
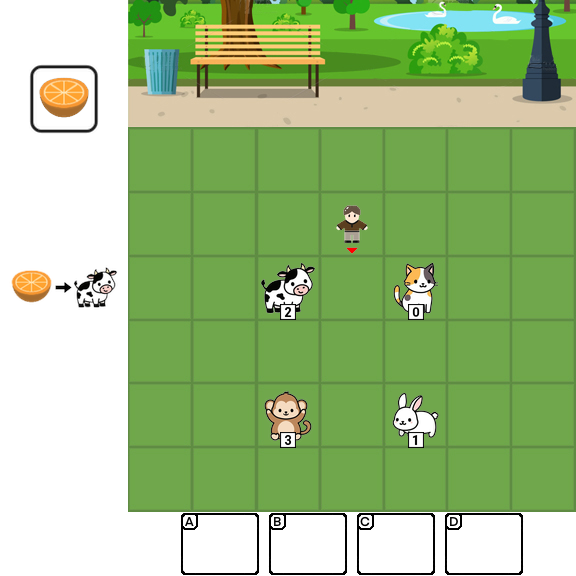
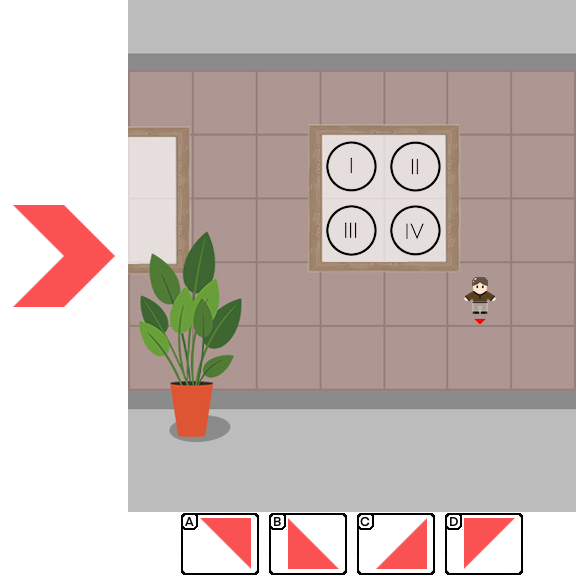
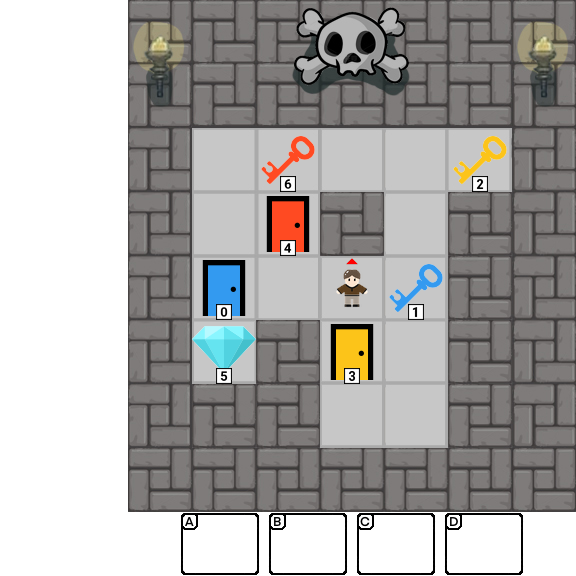
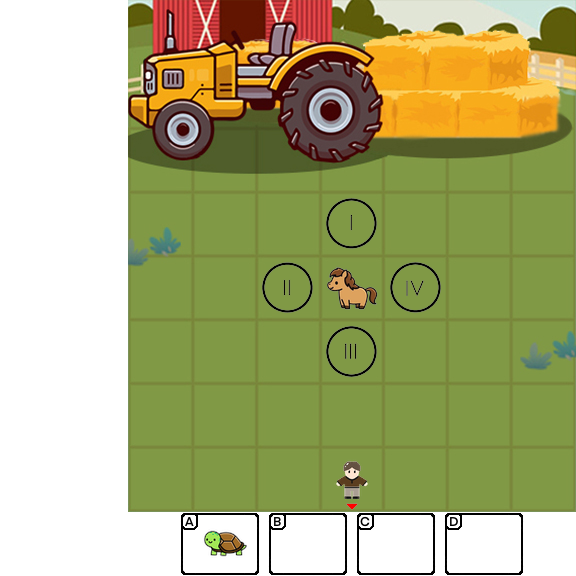
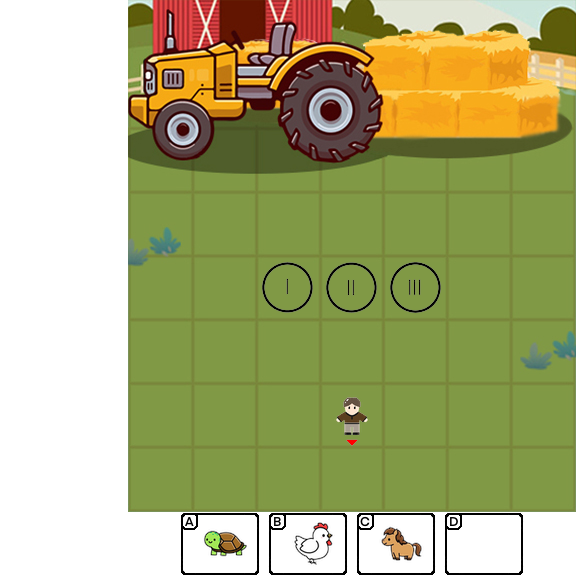
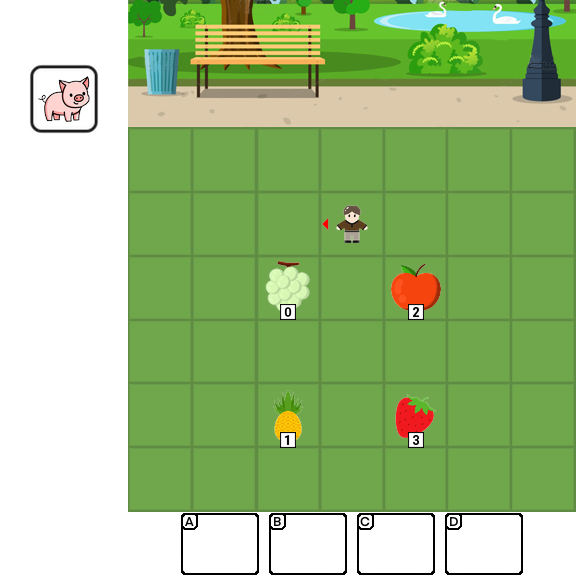
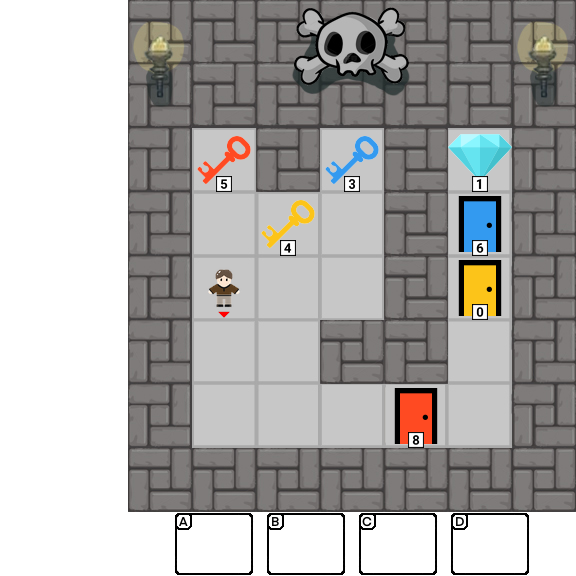
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) combine the linguistic strengths of LLMs with the ability to process multimodal data, enabling them to address a broader range of visual tasks. Because MLLMs aim at more general, human-like competence than language-only models, we take inspiration from the Wechsler Intelligence Scales — an established battery for evaluating children by decomposing intelligence into interpretable, testable abilities. We introduce KidGym, a comprehensive 2D grid-based benchmark for assessing five essential capabilities of MLLMs: Execution, Perception Reasoning, Learning, Memory, and Planning.
The benchmark comprises 12 unique tasks, each targeting at least one core capability, specifically designed to gauge MLLMs' adaptability and developmental potential, mirroring the stages of children's cognitive growth. Additionally, our tasks encompass diverse scenarios and objects with randomly generated layouts, ensuring a more accurate and robust evaluation of MLLM capabilities.
KidGym is designed to be fully user-customizable and extensible, allowing researchers to create new evaluation scenarios and adjust difficulty levels to accommodate the rapidly growing MLLM community. Through the evaluation of state-of-the-art MLLMs using KidGym, we identified significant insights into model capabilities and revealed several limitations of current models. We release our benchmark at: https://kidgym.github.io/KidGym-Website/.
Results
BibTeX
@inproceedings{ye2026kidgym,
title = {Children's Intelligence Tests Pose Challenges for MLLMs? KidGym: A 2D Grid-Based Reasoning Benchmark for MLLMs},
author = {Ye, Hengwei and Guan, Yuanting and Ge, Yuxuan and Zhu, Tianying and Guan, Zhenhan and Zhong, Yijia and Zhang, Yijing and Zhang, Han and Wu, Yingna and Tian, Zheng},
booktitle = {International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR)},
year = {2026}
}